General Surgery
Femoral Hernia Repair Treatment
Femoral Hernia Repair
When an internal part of the patient’s body pushes through a weakness in the muscle or the surrounding tissue wall, results in the hernia. The individual’s muscles are generally tight and strong enough to keep the organs and intestines in its place, but a hernia can be developed if there are any weak spots.
Introduction
When an internal part of the patient’s body pushes through a weakness in the muscle or the surrounding tissue wall, results in the hernia. The individual’s muscles are generally tight and strong enough to keep the organs and intestines in its place, but a hernia can be developed if there are any weak spots.
What is Femoral Hernia Repair Surgery?
Femoral hernias are just another type of groin hernias, but they occur lower in the body as compared to that common inguinal hernia. Femoral hernias develop in the upper part of the thigh near the groin just below the inguinal ligament, where abdominal contents pass through a naturally occurring weakness called the femoral canal. Because of the high incidence of complications, femoral hernias generally require emergency surgery.
Need for the Femoral Hernia Repair Treatment
Femoral hernias are common in women and as a rule, the patient experiences pain and discomfort, and if the hernia becomes incarcerated (the blood supply of the tissue being herniating is finally cut off – hence, causing the tissue to die), the situation becomes dangerous.
The Treatment is needed for:
-
Pain Relief: Femoral hernias may be symptomatic and characterized by tenderness and pain which may be precipitated by standing or straining. This pain can be relieved by repairing the hernia.
-
Prevent Complications: Femoral hernias have a higher propensity for complication than other hernias, particularly the strangulation type.
-
Restore Normal Function: Hernia repair allows completely normal movement without pain, for untreated hernias can restrict mobility and overall activity.
Symptoms of Femoral Hernia
A femoral hernia is usually a piece of tissue, commonly a segment of the intestine, which protrudes through a hole in the femoral canal. Some femoral hernias are asymptomatic or may be minimally symptomatic, yet they may cause pain and some severe problems.
Here are the typical symptoms:
- Small Lump near the Groin or Upper Thigh
- Pain or Discomfort in the Groin Area
- Abdominal Pain or Discomfort
- Sudden or Severe Pain
- Nausea and Vomiting
- Bowel Changes
Causes of femoral hernia repair
A femoral hernia is being caused when internal tissues pushing through a weak point in the muscle wall, near the inner thigh or the groin area. The exact cause may not be known to the doctors. Sometimes, the patients may have a structurally weak muscle wall in the area from birth.
Femoral hernias can also be caused by excess pressure or straining in the site due to:
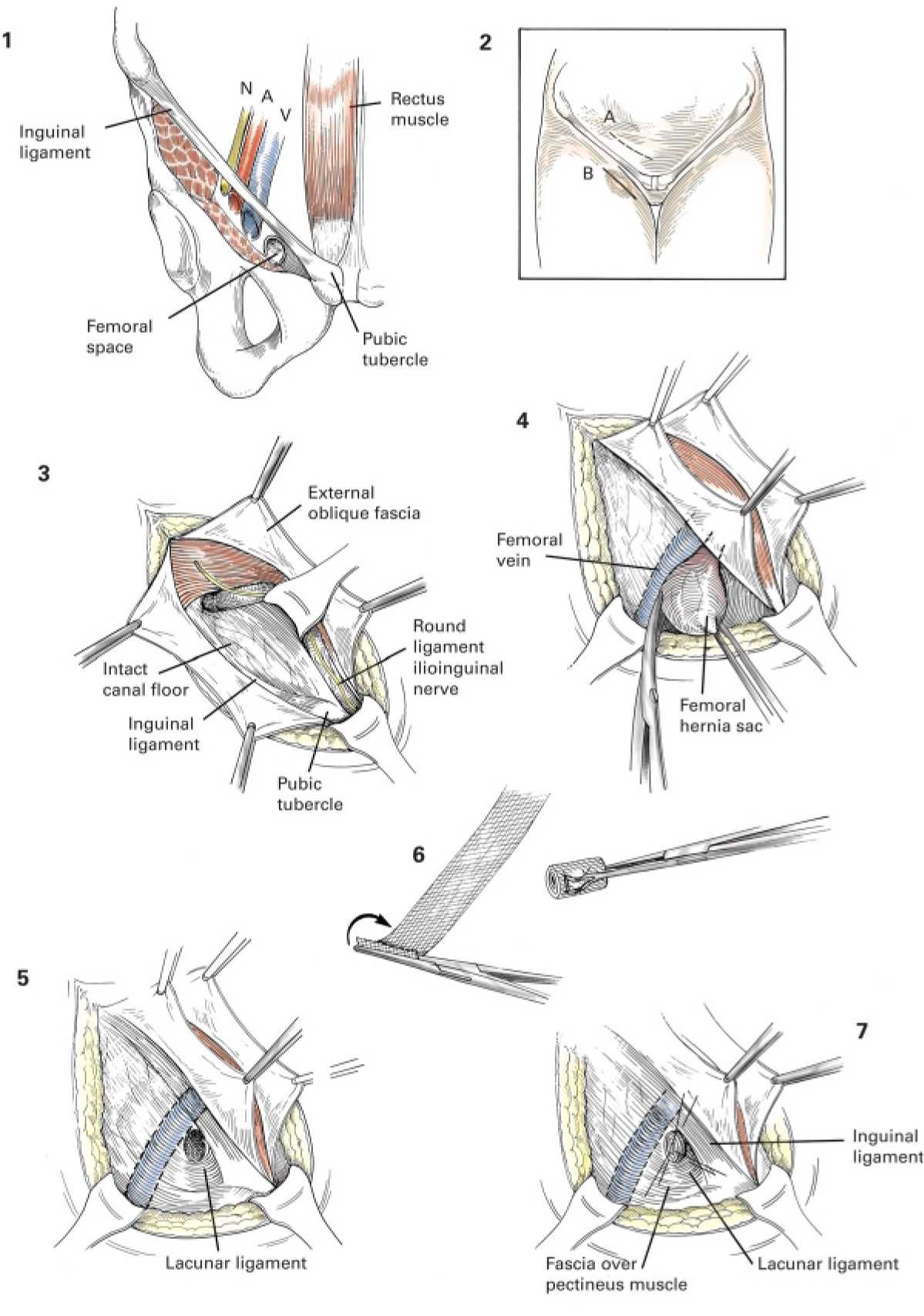
- Passing stool or urine
- Being obese
- Pushing or lifting heavy objects
- Having a persistent, strong cough
- Giving birth
- Having an abnormal buildup of abdominal fluid or an ascites
- Receiving treatment for kidney disease, or dialysis.
Facilities and Services Offered for International Patients for Femoral Hernia Repair Treatment
There are many hospitals for femoral hernia repair treatment in the world; many of them have international facilities and services for the patient to make them feel comfortable. Here’s what many top healthcare facilities offer:
- Dedicated International Patient Departments
- Comprehensive Pre-Arrival Services
- Accommodation and Transportation Assistance
- Interpreter Services
- Post-Surgery and Recovery Support
- Tourist and Cultural Amenities
- Safety and Emergency Care
Pre-Treatment Process of Femoral Hernia
There are several things that must be done before the operation can be carried out on a patient with femoral hernia.
Here’s an overview of what to expect:
- Initial Consultation and Diagnosis
- Preoperative Health Assessment
- Patient Education and Counselling
- Lifestyle Adjustments before Surgery
- Preparing for Hospital Stay
- Day-before Preparations
- Final Preoperative Check
Diagnostic Tests for Femoral Hernia
In diagnosing femoral hernia and prior to surgery for femoral hernia repair, tests and examination may be performed in order to finalise a diagnosis, determine the severity of the hernia and plan the course of surgery.
Here are the primary diagnostic tests involved:
- Physical Examination
- Ultrasound
- Computed Tomography (CT) Scan
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)
- X-Ray (Abdominal)
- Blood Tests
- Differential Diagnosis
What are the risks involved?
Though the direct cause may not be known, some people are at higher risk as compared to the others.
Risk factors include:
Sex: Both male and female can develop a femoral hernia, but they occur in female approximately 10 times more the males. This is due to the fact that the female pelvis is wider than that of the male pelvis.
Age: Femoral hernias are more likely to occur in adults than in the children. If a child does develop one, it sometimes results from a medical condition, such as a connective tissue disorder.
Family history: People with a close family member who has a groin hernia have up to 8 times the risk of developing femoral hernia themselves.
Procedure
During the surgery for repairing of the hernia, the bulging tissues are pushed back in. The weakened area is strengthened or sewn closed. This repair can be done either with open or with the laparoscopic surgery.
In open surgery:
The patients may receive general anesthesia. The general anesthesia keeps the patients asleep and pain-free. Or, the patients may receive regional anesthesia, which numbs the patients from the waist to their feet. Or, the surgeon may choose to give the patients local anesthesia and medicine for relaxing them. The surgeon makes an incision in the patient’s groin site. The hernia is located and separated from the tissues surrounding it. Some of the extra hernia tissue may also be removed. The rest of the hernia contents are gently pushed back inside the patient’s abdomen. The surgeon then closes the patient’s weakened abdominal muscles with the help of the stitches. Generally, a piece of mesh is also sewn into place for strengthening the patient’s abdominal wall. This helps in repairing the weakness in the wall. After the repair is being done, the incisions are being stitched closed.
In laparoscopic surgery:
The surgeon makes three to five small incisions in the patient’s lower belly and groin. A medical instrument called a laparoscope, whose scope is thin, and has a lighted tube with a camera on it. The instrument is being inserted through one of the incisions. Laparoscope helps the surgeon to view the inside of the belly. Other tools are also being inserted through the other incisions. The surgeon uses these tools for repairing the hernia. The same repair will be performed as in the open surgery. After the repair has been performed, the scope and other tools will be removed. The incisions are being stitched closed.
Post-Treatment Process of Femoral Hernia
Post treatment management after femoral hernia repair is initial important step that can help one recover from the operation without any complications or extended stay in hospital.
Here’s a breakdown of what patients can expect after the procedure:
- Immediate Postoperative Care
- Hospital Stay and Discharge
- Activity and Mobility
- Diet and Hydration
- Follow-up Appointments
- Incision and Wound Care
- Pain Management and Medication
- Gradual Return to Normal Activity
- Recognizing Complications
- Long-Term Care and Lifestyle Changes
Risks and Complications when undergoing femoral hernia repair surgery:
Surgery for femoral hernia repair is generally safe and complications are very rare. But, some of the complications may include:
Risk of general anesthesia: Before the surgery is being performed, the anesthesiologist (a doctor who administers anesthesia) reviews the risks of anesthesia and asks the patients about medical history and allergies to some certain medications. Complications are most likely to occur in older people and those, who have other medical conditions. Common complications include vomiting, urinary retention, sore throat, headache, and nausea. More serious problems include stroke, pneumonia, blood clots in the legs, and heart attack.
Hernia recurrence: A hernia can reoccur to the individual several years after repair. Recurrence is the most common complication of inguinal hernia repair, resulting in the second operation of the patients.
Bleeding: Bleeding inside the cut is yet another complication of inguinal hernia repair. It can result in bluish discoloration and severe swelling of the skin around the cut. Surgery may be required for opening the cut and thus stopping the bleeding.
Painful scar: Sometimes people experience tingling, sharp in a specific site near the cut after it has been healed. The pain generally resolves with the time. Medicine may be injected in the site if the pain continues to persist.
Injury to internal organs: Although this complication is very rare, injury to the intestine, kidneys, nerves bladder and blood vessels leading to the internal female organs, legs, and vas deferens (vas deferens is the tube that carries sperm) can occur during hernia surgery and may lead to more surgery.
Success Rate of Femoral Hernia Repair
Femoral hernia repair is also successful with 90% success rate depending on the method of surgery and patient characteristics. Recurrence rates are low, normally ranging from 1-5% greater if mesh reinforcement was used which shows overall effectiveness of the technique.
How soon will I recover?
The patients recovering from a femoral hernia repair can usually go home the same day as the surgery is performed or the day after.
During recovery people will generally need to:
- The patients can take pain medication to alleviate the discomfort.
- Restrict the patient’s movements and activities for several days.
- The patients must eat a healthful diet to prevent constipation and straining.
- The patients must take care of the wound.
- Recovery form femoral hernia repair can usually take up to 6 weeks, but most of the people return to light activities after rest of two weeks or so.
Best Hospitals for Femoral Hernia Repair
- Fortis Memorial Research Institute, Gurgaon
- Medanta The Medicity, Gurugram
- Artemis Hospital, Gurugram
- Max Hospital, Delhi
- Apollo Hospitals, Delhi
- BLK-Max Super Speciality Hospital, Delhi
Best Doctors for Femoral Hernia Repair
- Dr. Amit Javed
- Dr. Adarsh Choudhary
- Dr. Paritosh S Gupta
- Dr. Pradeep Chowbey
- Dr. Deepak Govil
- Dr. Deep Goel
Why Choose GetWellGo for Femoral Hernia Repair Treatment?
These are the some of the benefits accruable from seeking femoral hernia repair treatment from GetWellGo because this company can assist international patients in the following ways; here are key reasons why GetWellGo might be an excellent choice for femoral hernia repair:
- Specialized Medical Expertise
- Comprehensive International Patient Services
- Pre-Arrival and Travel Support
- Transparent and Affordable Pricing
- Comprehensive Postoperative Care
- Enhanced Patient Comfort and Convenience
- Travel and Accommodation
- Medical Visa Assistance
Conclusion
Femoral hernia repair is an effective intervention of hernia management, where patients gain almost immediate pain relief with gradual functional recovery. Its recurrence and complications are very low especially if good surgery procedures are followed. Patients are also told to lose weight, not to lift heavy objects or they should exercise good techniques of lifting objects. Many repairs give a cure that is permanent and patients are often seen regularly for follow up even when they are mobile.
FAQs
1. What anaesthesia is done?
- It is usually done under general anaesthesia, meaning that you will be unconscious during the period that the surgery is undertaking. For open surgery regional or local anaesthesia may be used and so although you are conscious you will not be able to feel anything in the area being operated on.
2. How long does the surgery last?
- The operation normally lasts about 30-45 minutes.
3. When can I go home?
- Shortly after the procedure is possible for most patients, and a few may be required to spend a night in the hospital.
5. What is next after surgery?
- Common symptoms include mild inflammation of the skin, bruise and soreness in the local area of surgery. They want you to take pain meds and to be careful. You should also do no vigorous exercise and limit the lifting of heavy loads much less for the next couple of weeks.
TREATMENT-RELATED QUESTIONS
GetWellGo will provide you end-to-end guidance and assistance and that will include finding relevant and the best doctors for you in India.
A relationship manager from GetWellGo will be assigned to you who will prepare your case, share with multiple doctors and hospitals and get back to you with a treatment plan, cost of treatment and other useful information. The relationship manager will take care of all details related to your visit and successful return & recovery.
Yes, if you wish GetWellGo can assist you in getting your appointments fixed with multiple doctors and hospitals, which will assist you in getting the second opinion and will help you in cost comparison as well.
Yes, our professional medical team will help you in getting the estimated cost for the treatment. The cost as you may be aware depends on the medical condition, the choice of treatment, the type of room opted for etc. All your medical history and essential treatment details would be analyzed by the team of experts in the hospitals. They will also provide you with the various types of rooms/accommodation packages available and you have to make the selection. Charges are likely to vary by the type of room you take.
You have to check with your health insurance provider for the details.
The price that you get from GetWellGo is directly from the hospital, it is also discounted and lowest possible in most cases. We help you in getting the best price possible.
No, we don't charge patients for any service or convenience fee. All healthcare services GetWellGo provide are free of cost.
Top Doctors for General Surgery
Top Hospitals for General Surgery
Contact Us Now!
Fill the form below to get in touch with our experts.







