Obstetrics and Gynaecology
Cesarean Delivery Treatment
Cesarean Section
A cesarean delivery (C-section or cesarean section), is the surgical procedure used to deliver a baby through incisions in the abdomen and uterus. Cesarean deliveries are generally avoided before 39 weeks of pregnancy so the child has healthy time to develop in the womb. Sometimes, however, complications arise and a cesarean delivery must be done prior to 39 weeks.
What is Cesarean delivery Treatment?
A cesarean delivery (C-section or cesarean section), is the surgical procedure used to deliver a baby through incisions in the abdomen and uterus. Cesarean deliveries are generally avoided before 39 weeks of pregnancy so the child has healthy time to develop in the womb. Sometimes, however, complications arise and a cesarean delivery must be done prior to 39 weeks.
A C-section might be planned ahead of time if the mother develops pregnancy complications or if she had a previous C-section and isn't considering a vaginal birth after cesarean.
Why Cesarean Delivery?
Sometimes a C-section is safer for the mother and for her baby than a vaginal delivery. The patient health care provider might recommend a C-section-
- If the labor isn't progressing. Stalled labor is one of the most prominent reasons for a C-section. Stalled labor might occur if the mother’s cervix isn't opening enough despite strong contractions over several hours.
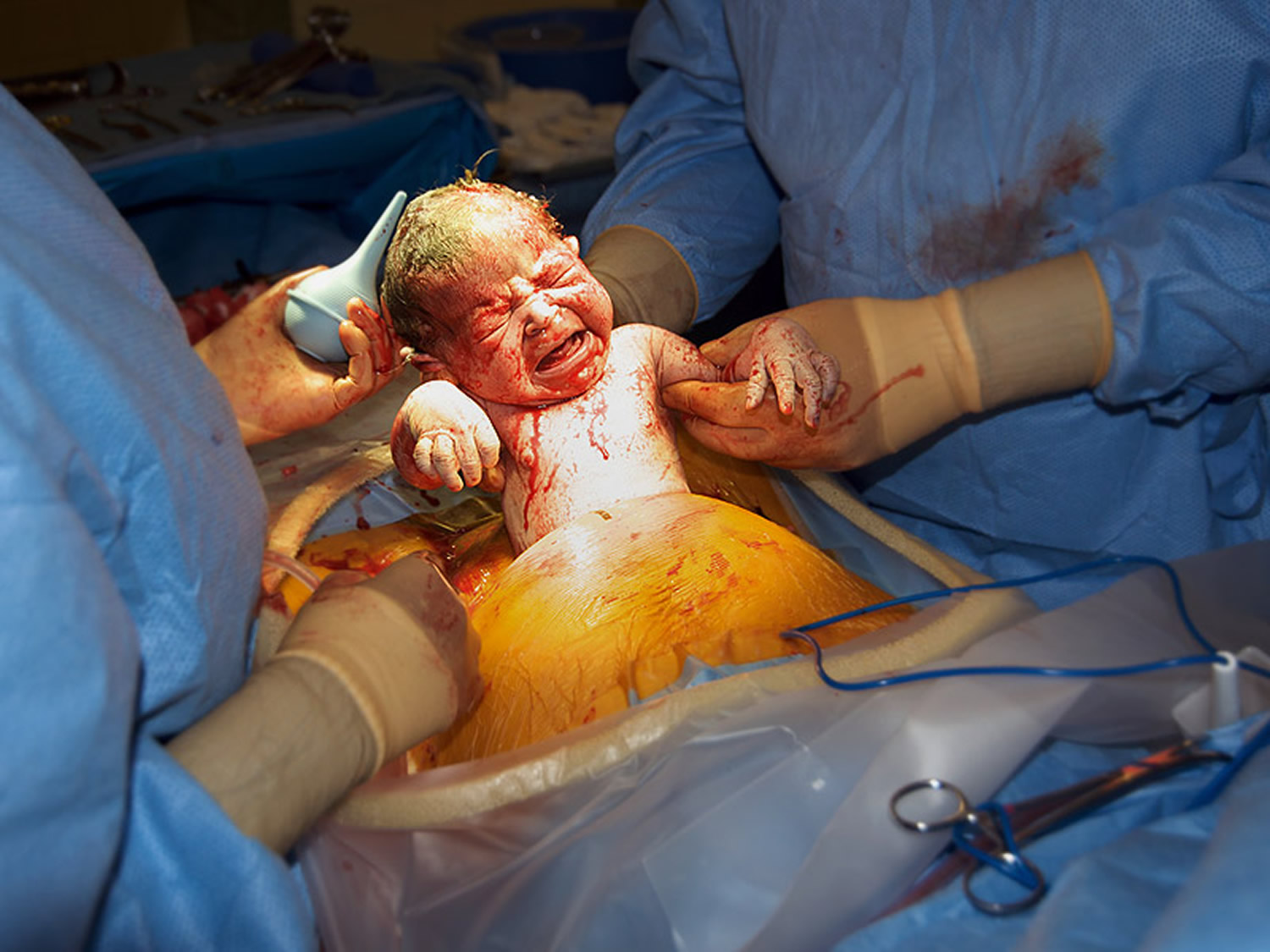
- If the baby is in distress. If the patient’s health care provider is concerned about changes in the baby's heartbeat, a C-section might be the best option.
- If the babies are in an abnormal position. A C-section might be the safest way to deliver the baby if the baby’s feet or buttocks enter the birth canal first or the baby is positioned side or shoulder first.
- If the mother is carrying multiples. A C-section might be needed if she is carrying twins and the leading baby is in an abnormal position or if she has triplets or more babies.
- If there's a problem with the placenta. If the placenta covers the opening of the cervix, then a C-section is recommended for delivery.
- If the umbilical cord is prolapsed, then a C-section might be recommended if a loop of umbilical cord slips through the cervix ahead of the baby.
- Mother’s health concern. A C-section might be recommended if the mother has a severe health problem, such as a heart or brain condition. A C-section is also recommended if she has an active genital herpes infection at the time of labor.
- Mechanical obstruction., the patient might need a C-section if she has a large fibroid obstructing the birth canal, a severely displaced pelvic fracture or the baby has a condition that can cause the head to be unusually large than normal.
- If the patient has a previous history with C-section, depending on the type of uterine incision and other factors, it's often possible to attempt a VBAC.
What are the risks involved?
Like other types of major surgery, C-sections also have risks.
Risks to baby:
- Breathing problems: Babies born by scheduled C-section have more chances to develop transient tachypnea, a breathing problem marked by abnormally fast breathing during the first few days after the birth.
- Surgical injury: Although very rare, accidental cut to the baby's skin can occur during surgery.
Risks to the mother:
- Infection: After a C-section, the patient might be at risk of developing an infection of the lining of the uterus.
- Postpartum hemorrhage: A cesarean delivery might cause heavy bleeding during and after delivery.
- Reactions to anaesthesia: Adverse reactions to any type of anaesthesia are possible which can be harmful.
- Blood clots: A cesarean delivery might increase the risk of developing a blood clot inside the deep vein, especially in the legs or pelvic organs. If a blood clot travels to the lungs and blocks blood flow, the damage can be life-threatening.
- Wound infection: Depending on the risk factors and whether the mother needs an emergency C-section, she might be at increased risk of an incision infection.
- Surgical injury: Although very rare, surgical injuries to the bladder or to the bowel can occur during a C-section. If there is a surgical injury during cesarean delivery, additional surgery might be required.
- Increased risks during future pregnancies: After a C-section, the patient faces a higher risk of potentially serious complications in a subsequent pregnancy than in a vaginal delivery. More the C-sections the patient have, higher the risks of placenta previa and a condition in which the placenta becomes abnormally attached to the wall of the uterus.
C-Section Delivery Procedure
Most cesarean surgery is carried out under spinal or epidural anaesthetic, this means the patient will be awake, but the lower part of her body is numbed so that she won't feel any pain.
During the C-section delivery procedure:
- A screen is placed across the body so that she can't see what's being done; the doctors and nurses will be updating the patient time to time.
- A cut of about 10-20cm long will be made across her lower tummy and womb so the baby can be delivered
- The patient may feel some tugging and pull during the procedure.
The whole operation usually takes about 40-50 minutes. Occasionally a general anaesthetic may be used, only if the baby needs to be delivered more quickly.
Future Pregnancies after a cesarean
- If the patient has a baby by cesarean, it doesn't necessarily mean that any babies she has in the future will also have to be delivered this way.
- Most women who have had a cesarean delivery can safely have a vaginal delivery for their next baby, known as vaginal birth after cesarean.
- However, the patient may need some extra monitoring during labor just to make sure everything is progressing well.
- Some women may be advised to have another cesarean if they are having another baby. This depends on whether a cesarean is still the safest option for the mother and for her baby.
Care of Mother after Cesarean Delivery
- Recovering from a cesarean usually takes longer time than recovering from a vaginal delivery.
- The patient might need to stay in the hospital for three or four days, compared with one or two days for a vaginal birth.
- The patient may experience some discomfort in her tummy for the first few days, and she'll be offered painkillers to cope with this.
- The wound in the tummy will eventually form a scar. This may be red and obvious at first, but it will fade with time and will often be hidden in the pubic hair.
Best Hospitals for Cesarean Section Treatment
- Fortis Memorial Research Institute, Gurgaon
- Medanta The Medicity, Gurgaon
- Artemis Hospital, Gurgaon
- Max Hospital, Saket, New Delhi
- Apollo Hospital, New Delhi
Best Doctors for Cesarean Section Treatment
- Dr. Mamta Pattnayak
- Dr. Preeti Rastogi
- Dr. Renu Raina Sehgal
- Dr. Anuradha Kapur
- Dr. Madhu Roy
Why Choose GetWellGo for Treatment of Cesarean Section?
Selecting the appropriate healthcare center that will attend to a mother during cesarean delivery is very important to both the mother and the child. Here are key reasons why GetWellGo may stand out as an excellent choice for cesarean delivery:
- Expert Medical Team
- Advanced Operation Theatres
- Neonatal Intensive Care Unit
- Pre-Surgery Counselling
- Postpartum Support
- Follow-up Appointments
- Transparent Pricing
- Language Support
- Travel and Accommodation Services
- Visa Assistance
FAQ
1. What are the advantages of cesarean section?
- Safety: Reduces risk in high risk pregnancies or in emergencies.
- Predictability: The date of delivery sometimes can be planned especially when the process to be undertaken is a planned C-section.
- Avoids Labor Complications: Disposes with the attached risks such as abnormal labor or birth injuries.
- Controlled Environment: Operation is conducted in a well-equipped theatre or operative room.
2. What is the success rate for cesarean delivery?
- Cesarean sections are quite frequent and compared to a great extent considered as safe with overall effectiveness in more than 95% of the healthcare facilities. The results are contingent upon the condition of the mother and the new-born as well as the needs, which underlie C-section.
3. How long does it take before a woman is discharged after a cesarean delivery?
- Hospital Stay: The recovery process takes 2 – 4 days, depending on the health of the human body and the progress of the workouts.
- Full Recovery: For most mothers’ relief, six to eight weeks is considered appropriate, while soreness may last considerably longer.
TREATMENT-RELATED QUESTIONS
GetWellGo will provide you end-to-end guidance and assistance and that will include finding relevant and the best doctors for you in India.
A relationship manager from GetWellGo will be assigned to you who will prepare your case, share with multiple doctors and hospitals and get back to you with a treatment plan, cost of treatment and other useful information. The relationship manager will take care of all details related to your visit and successful return & recovery.
Yes, if you wish GetWellGo can assist you in getting your appointments fixed with multiple doctors and hospitals, which will assist you in getting the second opinion and will help you in cost comparison as well.
Yes, our professional medical team will help you in getting the estimated cost for the treatment. The cost as you may be aware depends on the medical condition, the choice of treatment, the type of room opted for etc. All your medical history and essential treatment details would be analyzed by the team of experts in the hospitals. They will also provide you with the various types of rooms/accommodation packages available and you have to make the selection. Charges are likely to vary by the type of room you take.
You have to check with your health insurance provider for the details.
The price that you get from GetWellGo is directly from the hospital, it is also discounted and lowest possible in most cases. We help you in getting the best price possible.
No, we don't charge patients for any service or convenience fee. All healthcare services GetWellGo provide are free of cost.
Top Doctors for Obstetrics and Gynaecology
Top Hospitals for Obstetrics and Gynaecology
Contact Us Now!
Fill the form below to get in touch with our experts.

.png)





